
Research
Experimental work in nuclear physics is often diverse; each experiment is somewhat unique, it uses different detectors, various measurement systems, and brings together new people.
In this section, you will find a selection of the most interesting recent results, including outcomes from international collaborations, results obtained in international laboratories, as well as findings from our own experimental facilities, particularly the good old U120M cyclotron.
Asymptotic Normalization Coefficient Investigation of the 17O(d, p) Transfer for Astrophysical Application to the 17O(n, α)14C Reaction at Low Energies
- Cooperation: INFN-LNS ad.
AGB stars - red giants in an advanced stage of development - are at the origins of many elements heavier than iron. Their production depends on the neutron density in the star. One of the reactions that should significantly deplete neutrons is 17O(n, α)14C. The study examined 4 states/resonances in 18O, which are key to this question. The combined approach using THM and ANC methods allows for more precise reaction rates and shows that some heavy isotopes (87Rb, 142Ce, 204Hg, etc.) are produced 10% - 20% more frequently than previously expected.
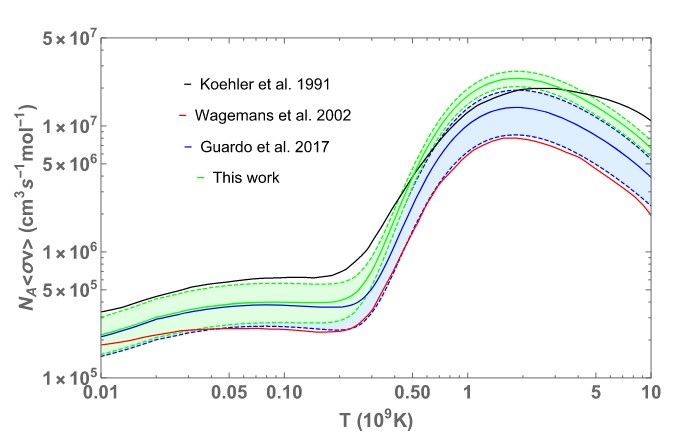
Fig.: Reaction rates of 17O(n, α)14C as a function of temperature (in billions of Kelvin). In green is the current result using the ANC method, in black and red are previous assumptions, in blue - the result using the THM method.
[1] G. L. Guardo et al., “Asymptotic Normalization Coefficient Investigation of the 17O(d, p) Transfer for Astrophysical Application to the 17O(n, α)14C Reaction at Low Energies,” ApJ, vol. 975, no. 1, p. 32, Oct. 2024, doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad7604.
Search for 22Na in novae supported by a novel method for measuring femtosecond nuclear lifetimes
Classical novae are thermonuclear explosions in stellar binary systems, and important sources of 26Al and 22Na. While γ rays from the decay of the former radioisotope have been observed throughout the Galaxy, 22Na remains untraceable. Its half-life (2.6 yr) would allow the observation of its 1.275 MeV γ-ray line from a cosmic source. However, the prediction of such an observation requires good knowledge of its nucleosynthesis. The 22Na(p, γ)23Mg reaction remains the only source of large uncertainty about the amount of 22Na ejected. Its rate is dominated by a single resonance on the short-lived state at 7785.0(7) keV in 23Mg. Here, we propose a combined analysis of particle-particle correlations and velocity-difference profiles to measure femtosecond nuclear lifetimes. The application of this method to the study of the 23Mg states, places strong limits on the amount of 22Na produced in novae and constrains its detectability with future space-borne observatories.
The authors report a particle-particle correlation and velocity-difference profile method to measure nuclear lifetime. The results obtained for excited states of 23Mg are used to constrain the production of 22Na in the astrophysical novae explosions.
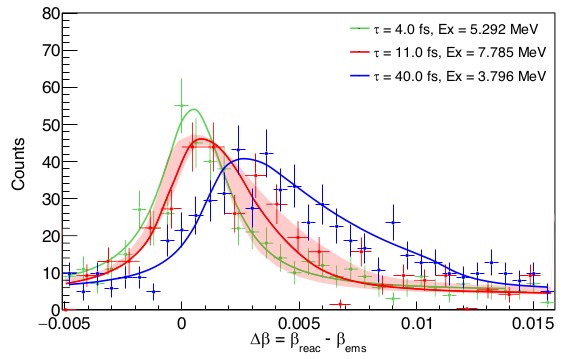
Fig.: Angle-integrated velocity-difference profiles. The 23Mg velocity at the time of reaction is shown against the velocity at the time of the γ-ray emission. The velocity profiles for the three states compared with simulations (continuous lines). It shows unambiguously that the key state (in red) has a lifetime 4 < τ < 40 fs. The red-shaded area corresponds to the simulations with lifetimes within 1σ uncertainty.
[1] C. Fougères et al., “Search for 22Na in novae supported by a novel method for measuring femtosecond nuclear lifetimes,” Nat Commun, vol. 14, no. 1, p. 4536, Sep. 2023, doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40121-3.
New narrow resonances observed in the unbound nucleus F-15
The structure of the unbound 15F nucleus is investigated using the inverse kinematics resonant scattering of a radioactive 14O beam impinging on a CH2 target. The analysis of 1H(14O, p) 14O and 1H(14O, 2p) 13N reactions allowed the confirmation of the previously observed narrow 1/2(-) resonance, near the two-proton decay threshold, and the identification of two new narrow 5/2(-) and 3/2(-) resonances. The newly observed levels decay by 1p emission to the ground of 14O, and by sequential 2p emission to the ground state of 13N via the 1(-) resonance of 14O. Gamow shell model (GSM) analysis of the experimental data suggests that the wave functions of the 5/2(-) and 3/2(-) resonances may be collectivized by the continuum coupling to nearby 2p- and 1p-decay channels. The observed excitation function 1H(14O, p) 14O and resonance spectrum in 15F are well reproduced in the unified framework of the GSM.
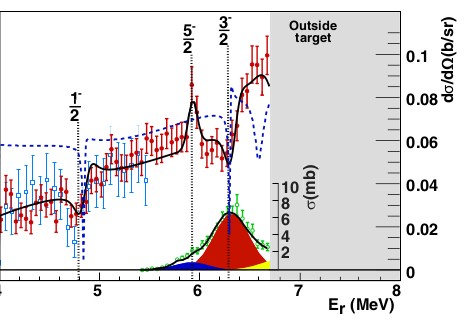
Fig.: Differential cross-section of the reaction H(14O, p)14O (red dots and blue squares) and the total cross-section of the reaction H(14O, 2p)13N (green circles), both as a function of the reconstructed resonance energy Er in the p+14O system. Contributions of the 5/2−, 3/2− states and higher-energy resonances are shown in blue, red, and green. The R-matrix fit of the two reaction channels is represented by a black line. The blue dashed line corresponds to the result of calculations using the GSMCC shell model.
[1] V. Girard-Alcindor et al., “New narrow resonances observed in the unbound nucleus 15F,” Phys. Rev. C, vol. 105, no. 5, p. L051301, May 2022, doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.105.L051301.
Neutron spectrum determination of accelerator-driven d(10)+Be neutron source using the multi-foil activation technique
Development of new fast neutron source based on cyclotron and beryllium target at NPI CAS studied. D(10)+Be source generated neutron energy spectra for two dist. (14mm, 154mm), and sets of Au, Co, Ti, In, Al, Fe, Ni, Nb irradiated. Neutron flux reached 1.4x1010 cm-2s-1 at 14mm, 4.1x108 cm-2s-1 at 154mm. Source offers activation analysis, neutron crosssec. data validation, simul. of exp. reactors, and material rad. hardness tests.
[1] M. Stefanik, E. Simeckova, P. Bem, J. Stursa, V. Zach, and J. Mrazek, “Neutron spectrum determination of accelerator-driven d(10)+Be neutron source using the multi-foil activation technique,” Radiation Physics and Chemistry, vol. 190, p. 109767, Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2021.109767.
Trojan Horse Investigation for AGB Stellar Nucleosynthesis
- Cooperation: INFN-LNS
AGB stars are key astrophysical sites influencing nucleosynthesis and chemical abundances. Nucleosynthesis requires experimentally-measured cross sections, obtained via the Trojan Horse Method and Asymptotic Normalization Coefficient indirect techniques. This report discusses the experimental procedure and deduced reaction rates. Studies of interest for AGB nucleosynthesis are also reported.
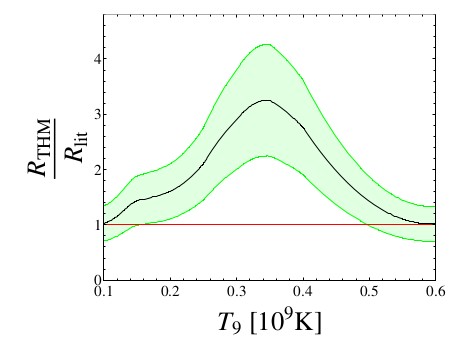
Fig.: Ratio of the 19F(α, p)22Ne THM reaction rate to the one calculated earlier (Rlit). The estimated uncertainties of the THM data are reported as a green band.
[1] M. L. Sergi et al., “Trojan Horse Investigation for AGB Stellar Nucleosynthesis,” Universe, vol. 8, no. 2, Art. no. 2, Feb. 2022, doi: 10.3390/universe8020128.
26Si(p,γ)27P direct proton capture by means of the asymptotic normalization coefficients method for mirror nuclei
- Cooperation: INFN-LNS
The radioactive isotope 26Al is observed along the Milky Way plane in γ-ray wavelength. Its origin has been heavily debated in the last 40 years. A detailed estimation of 26Al production in galaxy is complicated. This isotope is in part produced in the form of the isomer 26mAl, that is (because of its decay properties) invisible in the galaxy. We have investigated the reaction 26Si(p,γ), that reduces the production of the "invisible" 26mAl. We used the deuteron beams from U120-M cyclotron in NPI Rez and indirect method ANC applied on the mirror nuclus (26Mg). We thus obtained new information about 26Si(p,γ)27P reaction velocities.
[1] G. D’Agata et al., “26Si(p, γ)27P direct proton capture by means of the asymptotic normalization coefficients method for mirror nuclei,” Phys. Rev. C, vol. 103, no. 1, p. 015806, Jan. 2021, doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.103.015806.
Deuteron-induced reactions on natural Zr up to 60 MeV
Future energetic devices based on fusion or fission need reliable data on activation of construction/target materials. Reactions induced by deuterons are difficult to describe theoretically, because many processes are involved. We have experimentally studied Zircon activation on the deuteron beam of U120-M cyclotron of NPI Rez, we obtained new data and clarified a previously unclear situation in production of Nb isotopes. The all available data were included in the complex analysis and consistently described by a combination of competing reaction mechanisms (break-up, direct, compound, pre-equilibrium).
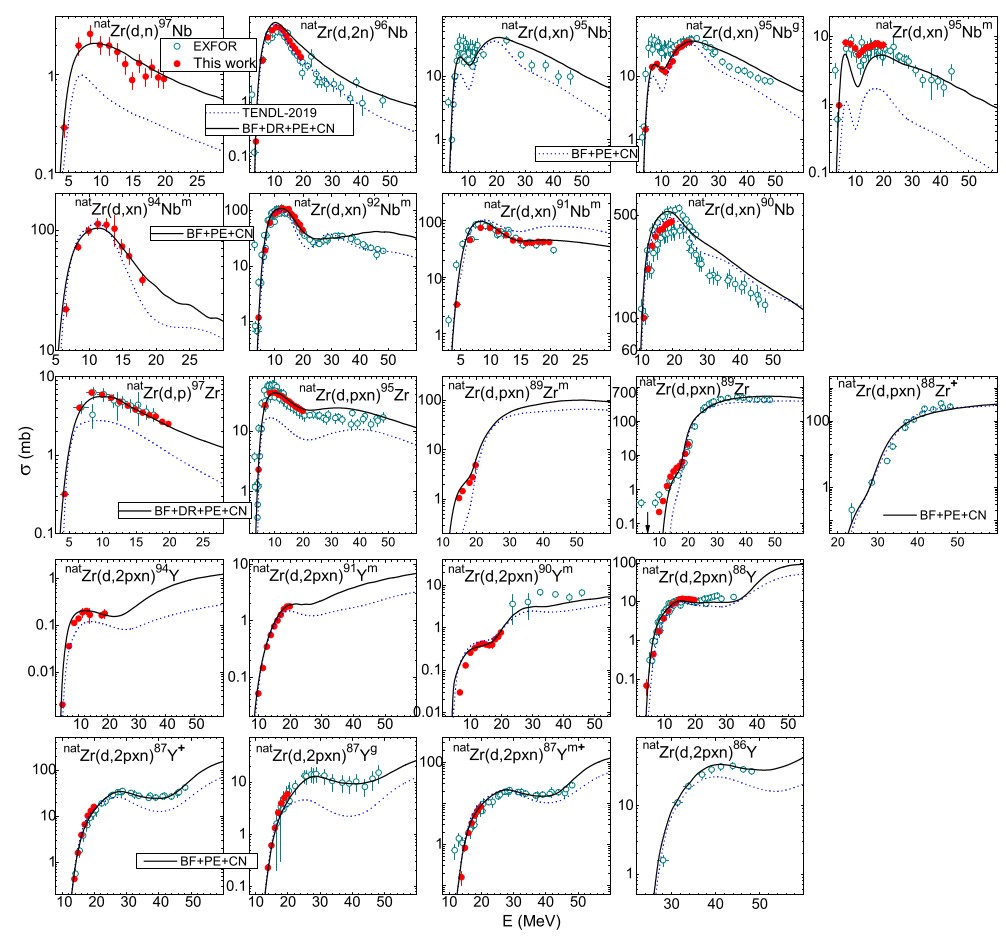
Fig: Energy dependence of activation cross-section of deuteron-induced reactions on Zr. Red points - our measurements, solid lines - our calculations.
[1] E. Šimečková et al., “Deuteron-induced reactions on natZr up to 60 MeV,” Phys. Rev. C, vol. 104, no. 4, p. 044615, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.104.044615.
Probing nuclear forces beyond the nuclear drip line: the cases of 16F and 15F
- Cooperation: GANIL/SPIRAL2
Nuclei that are far from stability provide us an opportunity to enhance our understanding to the properties of the nuclear matter. Fluorine isotopes 15F and 16F (proton-rich) are unbound. Several experiments using the resonant elastic scattering method were performed at GANIL with radioactive beams to determine the properties of the low lying states of these nuclei. Strong asymmetry between 16F - 16N and 15F - 15C mirror pairs is observed. For 16N-16N, the asymmetry can be explained by the effect of distribution of nucleons. But not in the second case, on contrary, this might be an indication of a new effect - e.g. an enhanced two-proton correlation in the 15F nucleus.
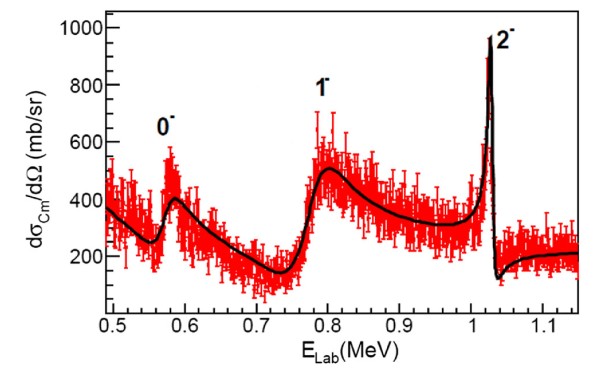
Fig.: Excitation function of 15O(p,p’) reaction (from our previous work). Three states (resonances) in 16F nucleus are clearly visible. The solid line is a theoretical description.
[1] V. Girard-Alcindor et al., “Probing nuclear forces beyond the nuclear drip line: the cases of 16F and 15F,” Eur. Phys. J. A, vol. 57, no. 3, p. 93, Mar. 2021, doi: 10.1140/epja/s10050-021-00410-1.
Astrophysical S-factor for the 3He(α, γ)7Be reaction via the asymptotic normalization coefficient (ANC) method
- Cooperation: ATOMKI, INFN-LNS
The detection of the neutrinos produced in the p−p chain and in the CNO cycle can be used to test the Standard Solar Model. The 3He(α,γ)7Be reaction is the first reaction in two branches of the p−p chain, its cross section influences the prediction of the 7Be and 8B neutrino fluxes. A better accuracy of the reaction cross section is needed. In the work the reaction was studied using the Asymptotic Normalization Coefficient (ANC) technique and the astrophysical S-factor was measured with the desired precision.
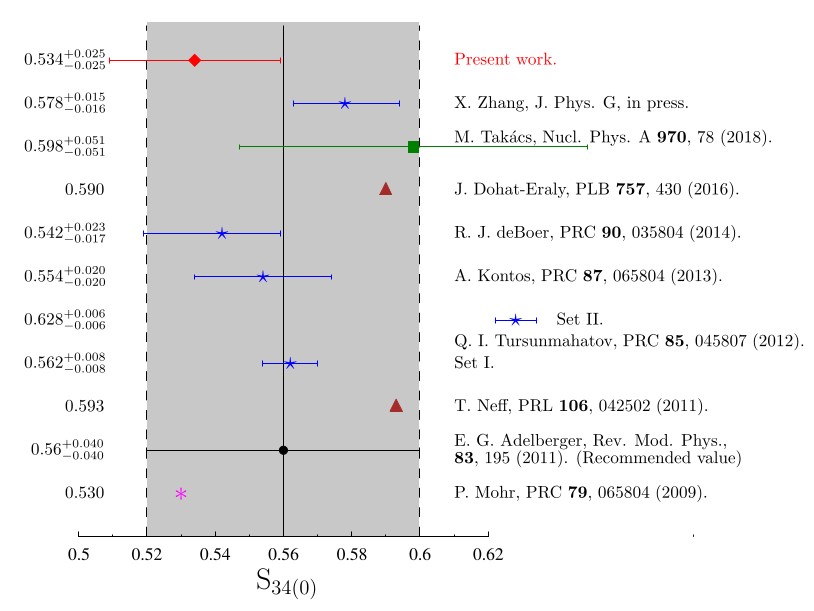
Fig.: Summary of the most recent 3He(α,γ)7Be S-factor results. The red diamond is the current measurement, the solid central line represents the recommended value, with its uncertainty indicated with the shaded area.
[1] G. G. Kiss et al., “Astrophysical S-factor for the 3He(α,γ)7Be reaction via the asymptotic normalization coefficient (ANC) method,” Physics Letters B, vol. 807, p. 135606, Aug. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.physletb.2020.135606.
Deuteron-induced reactions on manganese at low energies
- Cooperation: IFIN/HH
The scarce data systematics and complexity of deuteron interactions demand both experimental and theoretical efforts in measurements of activation cross sections. Reactions induced by neutrons and protons following the breakup must be also taken into account. Activation cross sections of 54,56Mn and 51Cr nuclei by deuterons on 55Mn were measured at energies around 20 MeV. Major discrepancies in the current evaluations are found to lie in the missing proper account of direct interactions.
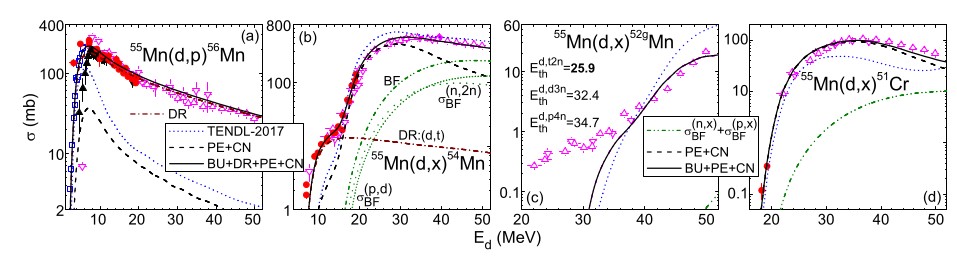
Fig.: Previous and present data (red circles) and present calculated results (solid curves). Different reaction components (PE, CN, DR, BU) are presented.
[1] M. Avrigeanu et al., “Deuteron-induced reactions on manganese at low energies,” Phys. Rev. C, vol. 101, no. 2, p. 024605, Feb. 2020, doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.101.024605.
Indirect measurement of the 3He(n, p)3H reaction cross section at Big Bang energies
- Cooperation: INFN-LNS
Nuclear reactions play a key role in the framework of the Big Bang Nucleosynthesis. A network of 12 principal reactions has been identified as the main path of the nucleosynthesis in the first 20 min of the history of the Universe. Big efforts in the last decades have led to a better understanding of the role of neutron-induced reactions in the primordial nucleosynthesis. We applied the Trojan Horse Method to extract the cross section at astrophysical energies for the 3He(n,p)3H reaction.
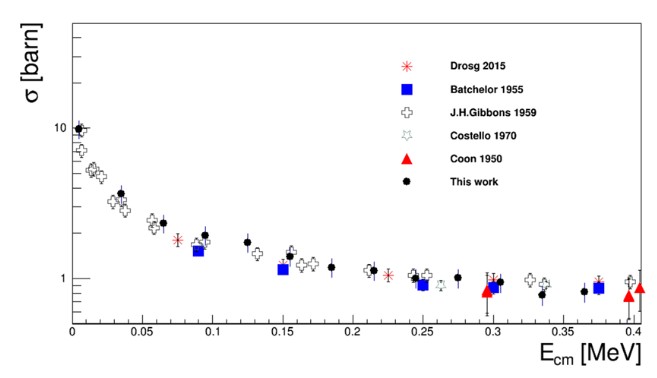
Fig.: Binary cross section (black circles) after including the penetration factor and normalized to direct data for the 3He(n,p)3H reaction extracted via THM method. Only errors from statistics and normalization are shown.
[1] R. G. Pizzone et al., “Indirect measurement of the 3He (n,p) 3H reaction cross section at Big Bang energies,” Eur. Phys. J. A, vol. 56, no. 8, p. 199, Aug. 2020, doi: 10.1140/epja/s10050-020-00212-x.
Cross-section Measurement of the Cosmologically Relevant Be-7(n, alpha)He-4 Reaction over a Broad Energy Range in a Single Experiment
Studying interactions of radioactive ions with neutrons is particularly demanding. The case of the 7Be destruction induced by the (n,alpha) reaction is investigated at the energies typical of the primordial nucleosynthesis by means of the Trojan Horse Method applied to the 2H(7B,α - α)p quasi-free reaction. The 7Be(n,α)4He cross-section has been measured down to cosmological energies. The deduced reaction rate has the impact on big bang nucleosynthesis and on the lithium problem.
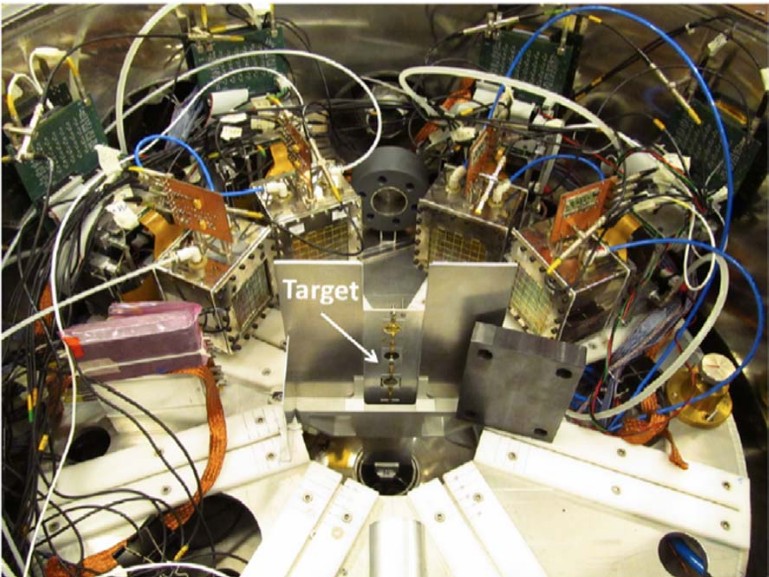
Fig.: Detector setup in vacuum chamber EXOTIC v INFN-LNS.
[1] L. Lamia et al., “Cross-section Measurement of the Cosmologically Relevant 7Be(n, α)4He Reaction over a Broad Energy Range in a Single Experiment,” ApJ, vol. 879, no. 1, p. 23, Jun. 2019, doi: 10.3847/1538-4357/ab2234.
Normal and intruder configurations in Si- 34 populated in the beta(-) decay of Mg-34 and Al-34
The structure of 34Si was studied through gamma spectroscopy separately in the β- decays of 34Mg and 34Al. The work studied spectroscopic properties of 34Si. A total of 11 newly identified levels and 26 transitions were added to the previously known level scheme of 34Si. Large scale shell-model calculations are compared with the new results and conclusions are drawn on the level of mixing between normal and intruder configurations, and the absence of triaxial deformation in 34Si.
IFIN-HH, Bucharest, ISOLDE CERN Physical Review C 100, 034306 (2019), 10.1103/PhysRevC.100.034306
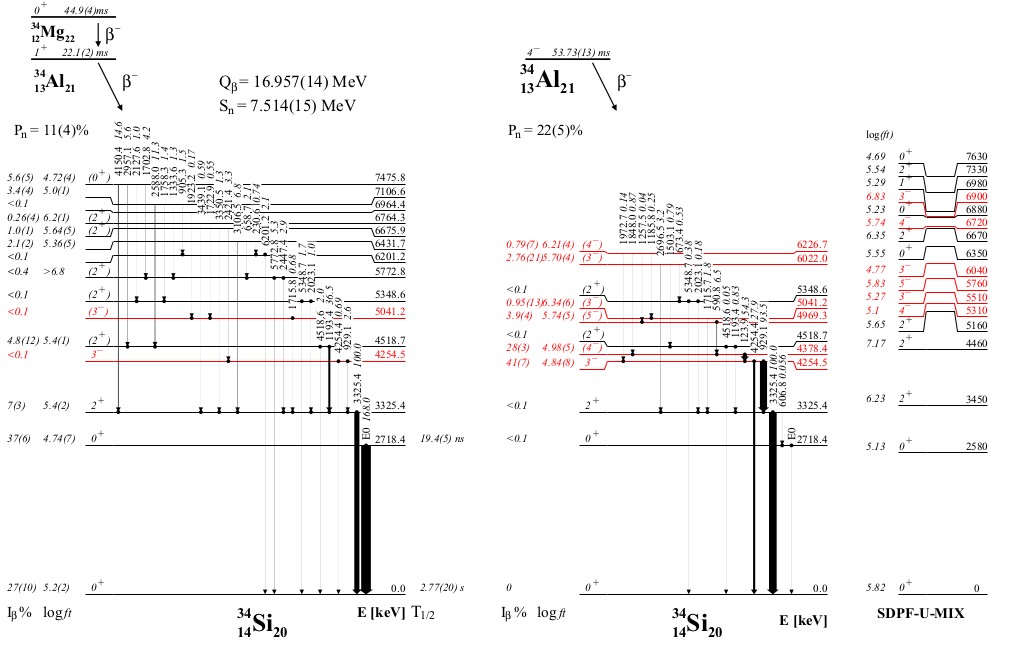
Fig.: Scheme of exited 34Si states with 11 new levels and 26 new transitions and SDPF-U-MIX model comparison. Negative parity levels in red.
[1] IDS Collaboration et al., “Normal and intruder configurations in 34Si populated in the β− decay of 34Mg and 34Al,” Phys. Rev. C, vol. 100, no. 3, p. 034306, Sep. 2019, doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.100.034306.
The determination of the astrophysical S-factor of the direct O-18(p, gamma)F-19 capture by the ANC method
- Cooperation: TA&MU, INFN LNS
The depletion of 18O via the (p, γ) capture competes with the (p, α) capture during the CNO cycles in AGB stars. While the (p, α) capture is dominant, the (p,γ) can play an important role in mixing stages of the AGB star evolution. We determined the astrophysical S-factor of the direct part of the 18O(p, γ)19F capture by the indirect method ANC and the direct contribution to the 18O(p, γ)19F capture process and were compared with the older mutually different results.
European Physical Journal A 55, 114 (2019), 10.1140/epja/i2019-12801-8
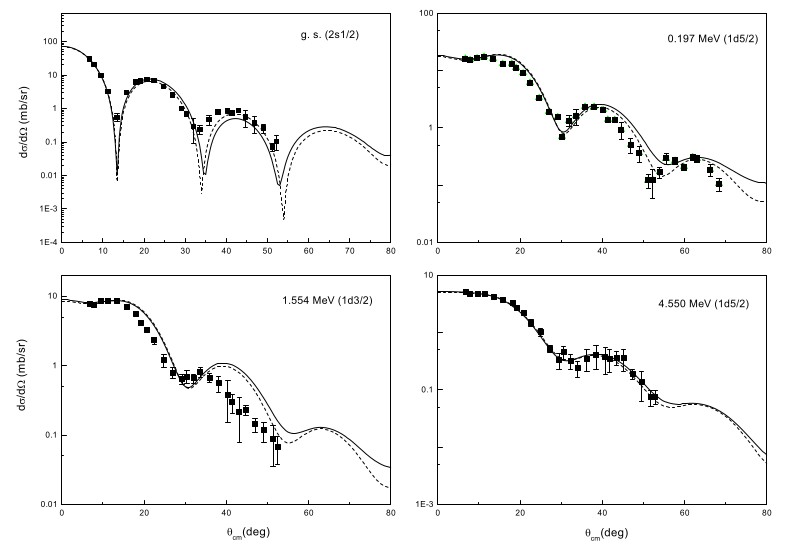
Fig.: Angular distribution of deuterons on four states of 19F from the reaction 18O(3He,d)19F, that was used to deduce the proton capture cross section on 18O.
[1] V. Burjan et al., “The determination of the astrophysical S-factor of the direct 18O(p,γ)19F capture by the ANC method,” Eur. Phys. J. A, vol. 55, no. 7, p. 114, Jul. 2019, doi: 10.1140/epja/i2019-12801-8.
Consistent account of deuteron-induced reactions on natCr up to 60 MeV
- Cooperation: IFIN HH, Romania
Reaction databases used in industry and applied research are based mainly on equilibrium and pre-equilibrium processes calculations. Experimentally discrepancies for Cr isotopes observed in NPI CAS in CANAM accelerator centre were described by direct processes as break-up and stripping. It was shown that these processes play an important role for all energies and reactions of deuterons with nuclei around energies of Coulomb barrier are to a large extent driven by direct processes.
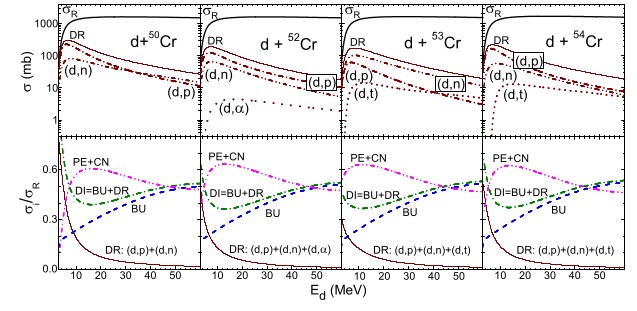
Fig.: Total reaction cross sections (full lines) are described as a sum of several different processes, that can be split to equilibrium (PE, CN) and direct (DR, BU). At low (Coulomb) energies, the direct processes (DR) play crucial role.
[1] E. Šimečková et al., “Consistent account of deuteron-induced reactions on natCr up to 60 MeV,” Phys. Rev. C, vol. 98, no. 3, p. 034606, Sep. 2018, doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.98.034606.
The intensities of γ-rays from the decay of 196m2Au
Due to their purity, gold foils are used as monitoring standard for neutrons. Gold foils were irradiated in NPI CAS in centre of accelerators CANAM. Isomers of radioactive isotope 196Au were produced and measured. Intensities of gamma transitions were measured with a larger accuracy and uncertainties were reduced (factor of several). This potentially means a reduction of uncertainties for future applications and measurements with neutrons.
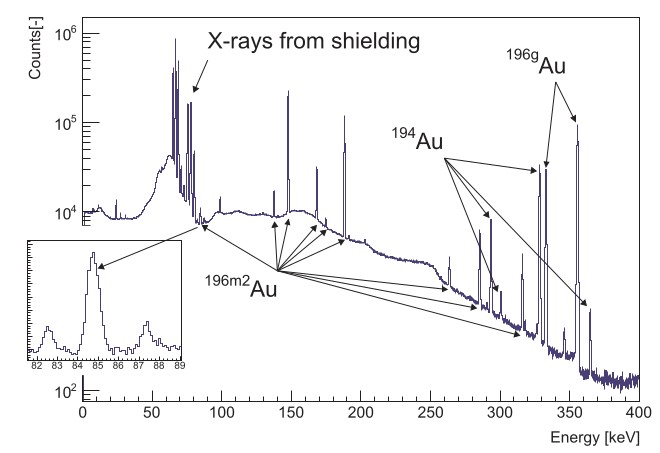
Fig.: Activated gold spectrum.
[1] M. Majerle et al., “The intensities of γ-rays from the decay of 196m2Au,” Applied Radiation and Isotopes, vol. 141, pp. 5–9, Nov. 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2018.07.026.
Investigation of the elastic and inelastic scattering of 3He from 9Be in the energy range 30–60MeV
- Cooperation: JINR Dubna
Nucleus of 9Be is an example of a so called Borromean system, where the nucleus is formed from 3 components (2x alpha and one neutron). In NPI CAS, centre of accelerators CANAM, we have measured the cross-sections for the elastic and inelastic scattering populating excited states in 9Be using 3He beams. The experimental results were analysed using the Woods–Saxon optical model, double-folding potentials and the coupled-channel method. The analysis shows that the excited state (5/2-) of 9Be is strongly deformed (beta=0.8).
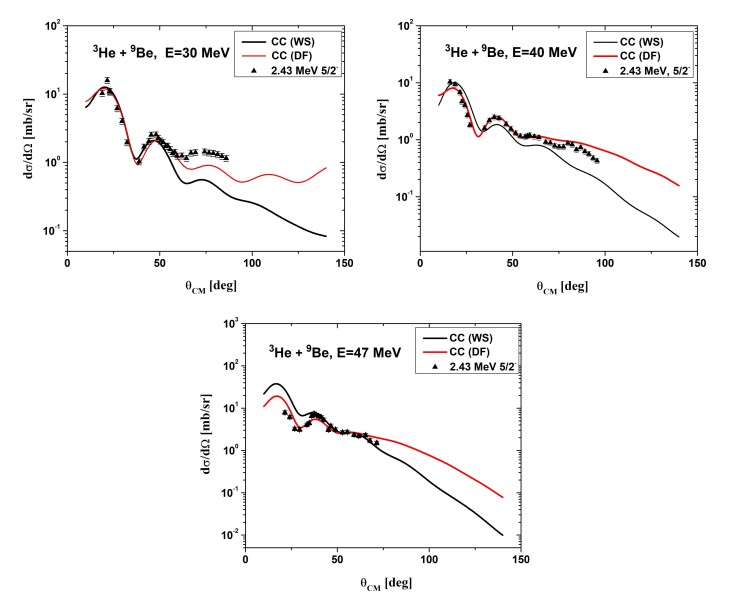
Fig.: Description of experimental points of angular distributions for level 5/2- of 9Be by Woods-Saxon and double folding (DF) potentials.
[1] D. M. Janseitov et al., “Investigation of the elastic and inelastic scattering of 3He from 9Be in the energy range 30–60MeV,” Int. J. Mod. Phys. E, vol. 27, no. 10, p. 1850089, Oct. 2018, doi: 10.1142/S0218301318500891.

